DROP SEIZURE REDUCTION
EPIDIOLEX®
(cannabidiol)
significantly reduced drop seizure frequency in patients living with LGS
A prespecified exploratory analysis evaluated the effect of EPIDIOLEX®
(cannabidiol)
on drop seizure reduction in the subgroup of patients receiving clobazam6
Adult patients: Reduction in drop seizure frequency with EPIDIOLEX®
(cannabidiol)7
Reduction in monthly frequency of drop seizures
Among patients taking clobazam, those also taking EPIDIOLEX experienced a greater reduction in drop seizures than with placebo6
Prespecified exploratory subgroup analysis: Drop seizure reduction in adult patients
Reduction in monthly frequency of drop seizures among adult patients7
Note: 49% of patients in LGS clinical trials were taking concomitant clobazam. Subgroup analysis is exploratory and descriptive in nature.
Note: Adult data represents ~1/3 of the total trial population.1,2 Subgroup analysis is exploratory and descriptive in nature.
Results from the 14-week treatment period. Drop seizures were defined as atonic, tonic, or tonic-clonic seizures that led to or could have led to a fall or injury.1,2
Patients at baseline1,2:
- Had previously tried a median of 6 prior ASMs
- Currently uncontrolled with a median of 3 current ASMs
94% of patients were taking ≥2 ASMs at baseline and still experiencing a median of 74 and 85 drop seizures (Study 1 and Study 2, respectively) per 28 days.1,2
The most commonly used concomitant ASMs were:
49% clobazam |
39% valproate |
33% lamotrigine
Reductions in drop seizure frequency were reported as early as Day 6 in a post hoc analysis of the LGS clinical trials.3
Recommended daily dosage is 10 mg/kg/day (5 mg/kg twice daily), with a maximum maintenance dosage of 20 mg/kg/day (10 mg/kg twice daily).
Administration of the 20 mg/kg/day dosage resulted in somewhat greater reductions in seizure rates than the recommended maintenance dosage of 10 mg/kg/day, but with an increase in adverse reactions. Patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment require a dose adjustment.
Important considerations for your patients taking EPIDIOLEX and clobazam:
- EPIDIOLEX can cause somnolence and sedation that generally occurs early in treatment and may diminish with continued treatment. These effects were more common in patients on concomitant clobazam
- Pneumonia was observed more frequently with concomitant use of EPIDIOLEX and clobazam
- Elevated ammonia levels have been reported in some EPIDIOLEX-treated patients who also had transaminase elevations. Most cases reported concomitant use of valproate, clobazam, or both
- Consider a reduction of dosage or discontinuation of clobazam if known clobazam adverse reactions occur
- Other CNS depressants, including alcohol, could potentiate the somnolence and sedation effect of EPIDIOLEX
- Monitor for somnolence and sedation and advise patients not to drive or operate machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on EPIDIOLEX
- Rapid withdrawal of ASMs can lead to increased seizure frequency and status epilepticus
Results from the 14-week treatment period. Drop seizures were defined as atonic, tonic, or tonic-clonic seizures that led to or could have led to a fall or injury.1,2
TOTAL SEIZURE REDUCTION
EPIDIOLEX®
(cannabidiol)
significantly reduced total seizures in patients living with LGS
A post hoc exploratory analysis evaluated the effect of EPIDIOLEX®
(cannabidiol)
on total seizure reduction in the subgroup of patients receiving clobazam6
Reduction in monthly frequency of total seizures
Among patients taking clobazam, those also taking EPIDIOLEX experienced a greater reduction in total seizures than with placebo6
Note: 49% of patients in LGS clinical trials were taking concomitant clobazam. Subgroup analysis is exploratory and descriptive in nature.
Results from the 14-week treatment period. Total seizures included drop and non-drop seizures.1,2
The baseline frequency of total seizures (median) in Study 1 was 177 in the placebo group and 145 in the EPIDIOLEX 20 mg/kg/day group.1
In Study 2, the baseline frequency of total seizures (median) was 181 in the placebo group, 165 in the EPIDIOLEX 10 mg/kg/day group, and 174 in the EPIDIOLEX 20 mg/kg/day group.2
Important considerations for your patients taking EPIDIOLEX and clobazam:
- EPIDIOLEX can cause somnolence and sedation that generally occurs early in treatment and may diminish with continued treatment. These effects were more common in patients on concomitant clobazam
- Pneumonia was observed more frequently with concomitant use of EPIDIOLEX and clobazam
- Elevated ammonia levels have been reported in some EPIDIOLEX-treated patients who also had transaminase elevations. Most cases reported concomitant use of valproate, clobazam, or both
- Consider a reduction of dosage or discontinuation of clobazam if known clobazam adverse reactions occur
- Other CNS depressants, including alcohol, could potentiate the somnolence and sedation effect of EPIDIOLEX
- Monitor for somnolence and sedation and advise patients not to drive or operate machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on EPIDIOLEX
- Rapid withdrawal of ASMs can lead to increased seizure frequency and status epilepticus
RESPONDER RATES
EPIDIOLEX®
(cannabidiol)
cut seizure frequency by ≥50% and ≥75% in more patients than placebo in the LGS trials
A prespecified exploratory analysis evaluated the effect of EPIDIOLEX®
(cannabidiol)
on seizure frequency in the subgroup of patients receiving clobazam6
Responder rates in adult patients taking EPIDIOLEX®
(cannabidiol)7
Responder rates (≥50% and ≥75% reductions in drop seizures from baseline)1,2
Among patients taking clobazam, those also taking EPIDIOLEX experienced a greater reduction in seizure frequency than with placebo6
Prespecified exploratory subgroup analysis: ≥50% seizure reduction in adult patients7
≥50% reduction in drop frequency from baseline among adult patients7
Note: 49% of patients in LGS clinical trials were taking concomitant clobazam. Subgroup analysis is exploratory and descriptive in nature.
Note: Adult data represents ~1/3 of the total trial population.1,2 Subgroup analysis is exploratory and descriptive in nature.
≥50% reduction in drop frequency from baseline among adult patients7
STUDY 1
STUDY 2
Note: 49% of patients in LGS clinical trials were taking concomitant clobazam. Subgroup analysis is exploratory and descriptive in nature.
Note: Adult data represents ~1/3 of the total trial population.1,2 Subgroup analysis is exploratory and descriptive in nature.
Results from the 14-week treatment period.1,2
More patients achieved freedom from drop seizures with EPIDIOLEX than with placebo.
4%
EPIDIOLEX
10 mg/kg/day
5%
EPIDIOLEX
20 mg/kg/day
0.6%
PLACEBO
Important considerations for your patients taking EPIDIOLEX and clobazam:
- EPIDIOLEX can cause somnolence and sedation that generally occurs early in treatment and may diminish with continued treatment. These effects were more common in patients on concomitant clobazam
- Pneumonia was observed more frequently with concomitant use of EPIDIOLEX and clobazam
- Elevated ammonia levels have been reported in some EPIDIOLEX-treated patients who also had transaminase elevations. Most cases reported concomitant use of valproate, clobazam, or both
- Consider a reduction of dosage or discontinuation of clobazam if known clobazam adverse reactions occur
- Other CNS depressants, including alcohol, could potentiate the somnolence and sedation effect of EPIDIOLEX
- Monitor for somnolence and sedation and advise patients not to drive or operate machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on EPIDIOLEX
- Rapid withdrawal of ASMs can lead to increased seizure frequency and status epilepticus
of patients in the LGS studies taking concomitant clobazam with either dose of EPIDIOLEX reported a dose reduction of clobazam during the trial.7
Results from the 14-week treatment period.1,2
3-YEAR OPEN-LABEL EXTENSION
3-year sustained reduction of drop seizures8
Open-label extension: Reduction in monthly frequency of drop seizures8
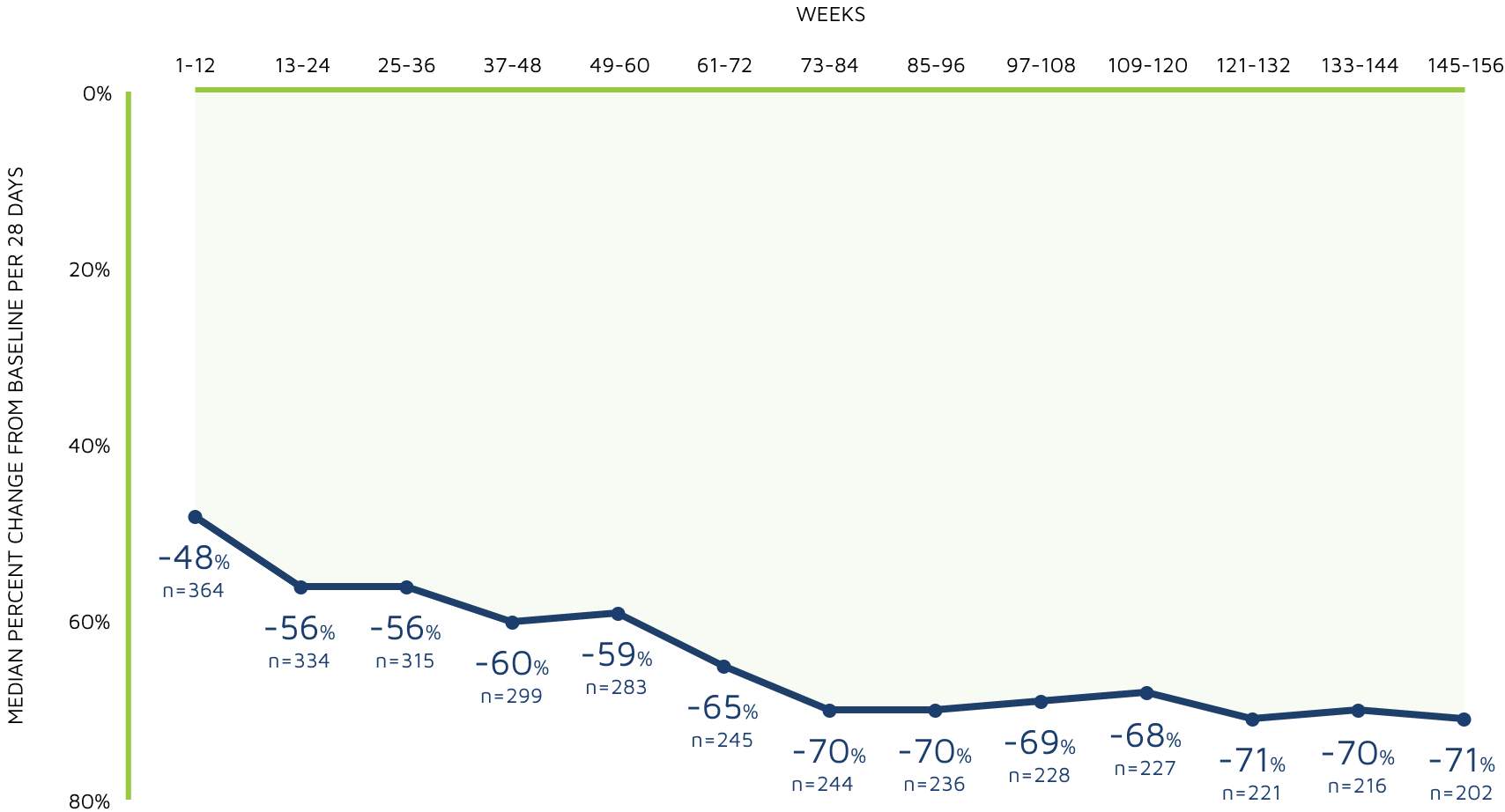
WEEKS

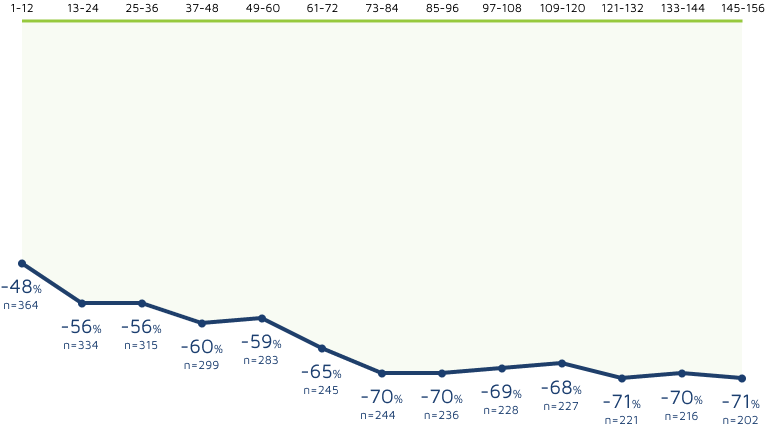
Decreasing n-values reflect a combination of discontinuations and rolling entry into the open-label extension trial.9
- Retention rates at 1, 2, and 3 years were 81%, 69%, and 65%, respectively9
- 30% (n=37) of withdrawals were due to adverse reactions8
- LOCF sensitivity analyses showed no impact of withdrawn patients on change in seizure frequency9
Reductions in total seizure frequency were also maintained with long-term treatment.8
Adverse events:
- The long-term safety profile of EPIDIOLEX® (cannabidiol)in this open-label extension trial was generally similar to that observed in the EPIDIOLEX clinical development program8
- Eleven deaths were reported in patients with LGS; none were deemed to be treatment-related by the investigator8
- In the open-label extension trial, titration to doses over 20 mg/kg/day was permitted. At higher doses, an increase in adverse reactions was observed8
of patients with LGS who completed controlled clinical trials chose to continue into theopen-labelextension.8
Additional resources

LGS caregiver-reported outcomes
Clinical studies assessed impression of change in overall condition, and a real-world survey assessed change in seizure and non-seizure outcomes with EPIDIOLEX.4,5
See results

A Potential Treatment Partnership for LGS
Dr. Benbadis discusses how EPIDIOLEX and another established ASM work together to potentially reduce seizures in LGS.
Watch now

EPIDIOLEX Experience
Follow investigative journalist Ashley Benecchi as she interviews epilepsy experts and caregivers of those living with refractory epilepsy.
Explore now